Scoliosis
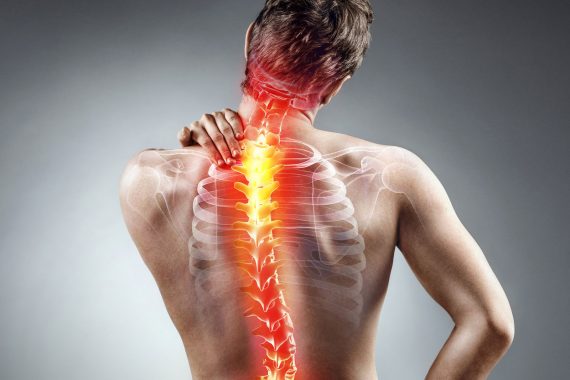
What Is Scoliosis?
Scoliosis is defined as the curvature of the spine over 10 degrees to the right or left, which should normally be placed in a straight line when the spine is viewed from the back.
Scoliosis is not just a one-dimensional angular deformation, but a bony and structural deformation that affects the body in three dimensions, from the front and from the side. Scoliosis is a condition that can be seen in every period of life.
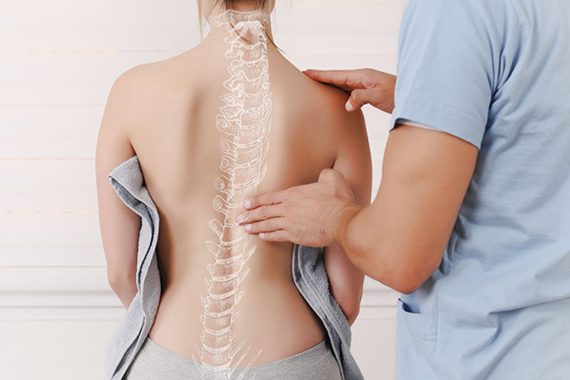
What are the Symptoms of Scoliosis ?
- Scoliosis leads to rapid deterioration (increase in curvature) with the starting of the adolescence. .
- Scoliosis progresses only in 10% of all patients’ and surgical treatment may be required.
- Diagnosing scoliosis can be done simply by visual inspection, so mothers suspect it during
- Usually no pain is felt.
- The curvature of the spine to the sides
- Lateral and forward curvature of the spine ,
- One shoulder (right-left) moving forward,
- Shoulders and hips are not symmetrical,
- Presence of a second curve compensating the first curvature,
- Back or lower back pain,
- Shortness of breath, tiredness,
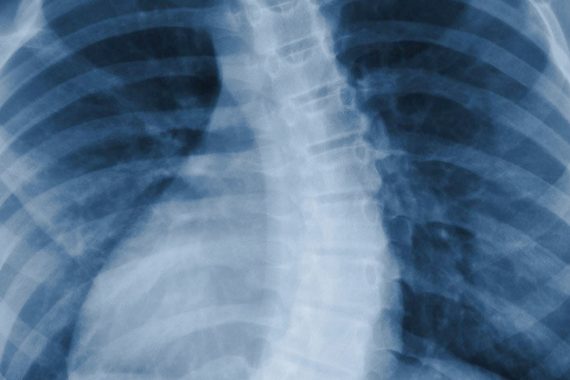
Scoliosis Treatment
Scoliosis treatment; It is planned by considering the age of the patients, the degree and location of the curvature, the severity of the pain in adults, the findings of physical examination and imaging methods, and the increase in the degree of curvature over time. Scoliosis X-ray and MUA until through early diagnosis subject, scoliosis rather increases the success of treatment.
Observation, corset treatment, physical therapy and surgical operation are applied in the treatment of scoliosis . Observation, which is the first option of treatment, is usually applied to curves below 20 degrees and shows how much the curvature has increased over time. Scoliosis physical therapy applications and surgical operations are particularly suitable for adults and more severe cases. However, surgical operations are the last to be used for the treatment of scoliosis in both children and adults.
